Toward Achieving Net-Zero in the Evolution of the Global Energy Sector
Keywords:
Net-Zero Emissions, Global Energy Transition, Decarbonization Pathways, Renewable Energy, Climate Policy ScenariosAbstract
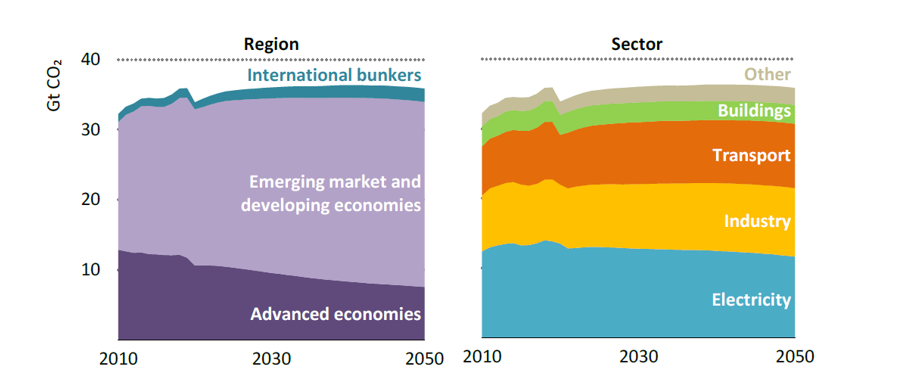
The transition to a net-zero emissions future represents one of the most significant challenges and imperatives facing the global energy sector. This article critically examines long-term trends and projections in total energy supply, final energy consumption, and electricity generation, while analyzing the associated implications for carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions under the Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS) and the Announced Pledges Scenario (APS). It explores the structural transformations occurring across regions and sectors, highlighting the divergence between advanced and developing economies in their decarbonization trajectories. The study emphasizes the accelerating electrification of end-use sectors, the evolving global fuel mix, and the role of renewables, bioenergy, nuclear, and fossil fuels in shaping energy futures. Significant disparities in energy access and technology readiness remain, particularly in emerging economies, posing challenges to equitable decarbonization. The article addresses Attaining net-zero emissions in the global energy sector requires a cohesive policy strategy that expedites clean energy implementation, improves overall efficiency, and guarantees fair involvement in the energy transition. The findings underscore that while the APS offers a more favorable outlook in emissions reduction and renewable energy penetration, substantial policy and technological efforts are still required to close the gap toward achieving the Paris Agreement goals.